Are you tired of long boot and loading times whenever you’re trying to game? Upgrading from an outdated HDD to a high-performance SSD will significantly reduce wait times and improve in-game performance.
What Is an SSD?
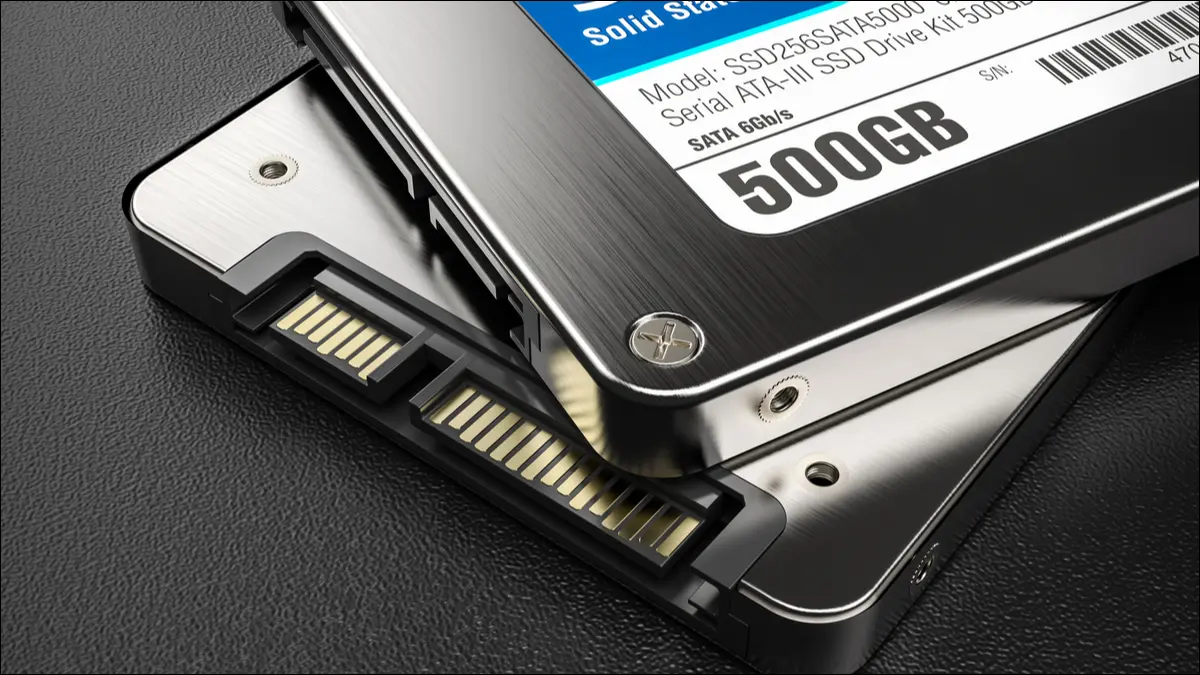
Without getting too technical, solid-state drives (SSDs) are a far improved type of storage device over traditional hard-disk drives (HDDs) that store and access data. Some SSDs provide large amounts of storage, however, they get far more expensive per gigabyte. SSDs are not new by any means as newer models are always coming out. For example, NVMe SSDs are completely outperforming older SSDs by miles.
SSDs perform the same functions as HDDs, but much faster. And even though they perform better, they also consume less power, around 30-60% less. So, by switching to an SSD, you’ll save quite a bit of energy over a year. An SSD is also more reliable and will last longer than hard drives. The bottom line is, that if you only use an HDD to run your games, you can greatly benefit by upgrading to an internal SSD. Or, if you can’t or don’t want to open up your PC, consider an external SSD.
Reduced Loading Times and Faster Booting
SSDs can easily improve your gaming experience in several ways. The most useful benefit is that they drastically reduce loading times and offer faster booting speeds. This includes everything from starting up your computer or console to waiting for a new map to load in your game.
No one likes waiting around, especially when all you want to do is jump into the action. If you’re tired of wasting minutes every day for your games and applications to load, then you’ll appreciate the quick booting and loading speeds that SSDs provide. This is thanks to their incredibly fast read and writes speeds, which allow them to upload and access stored data.
This doesn’t just apply to games as an SSD will speed up anything that requires loading data. Whether you’re starting an application or game, browsing the web, or loading a document or file, you’ll see a noticeable decrease in wait time. Saving a couple of seconds hundreds of times a day adds up, and it makes it feel like you’re using a brand new computer.
For comparison, HDDs have an average read and write speed of 80 to 160 mb/s. Meanwhile, SDDs’ read and write speeds start at 320 mb/s and can go as high as 7,000 mb/s or more. Samsung’s 980 PRO SSD provides up to 2TB of storage and has a read and write speed of 7,100 mb/s. This is about 89 times faster than your old and traditional hard-disk drive that has a read and writes speed of 80 mb/s.
Improved In-Game Performance
A responsive system is key for a smooth gaming experience, as even the smallest delay can cause you to miss a shot or make a bad move. When your system isn’t bogged down by loading times and other data-related issues, you’ll be able to play your games without unnecessary problems.
SSDs can improve your in-game performance by reducing or eliminating any stuttering, lagging, or frame rate issues that you might have been experiencing, especially if they were caused by a slow HDD. Can you recall all the times your game stutters whenever you venture into a new location? An SSD will help load all of your game files faster which can minimize performance issues.
If you tend to run games on high graphics that require a lot of data to be loaded into memory, an SSD will keep things running smoothly without hiccups. You’ll see a decrease in stuttering and frame rate drops because data is accessed much faster. Even if you’re playing less demanding games, you’ll still see a noticeable difference in performance thanks to the faster loading speeds that we mentioned earlier.
With an SSD, you may find that your game runs more smoothly overall, although it’s not guaranteed. You should also keep in mind that SSDs won’t increase frame rates. If you’re looking to improve your frames per second, you’ll need to invest in other hardware, such as a graphics card or CPU, or optimize your system for gaming. Also, if you continue to experience performance issues after installing an SSD, it’s likely to be another component that’s causing the problem.